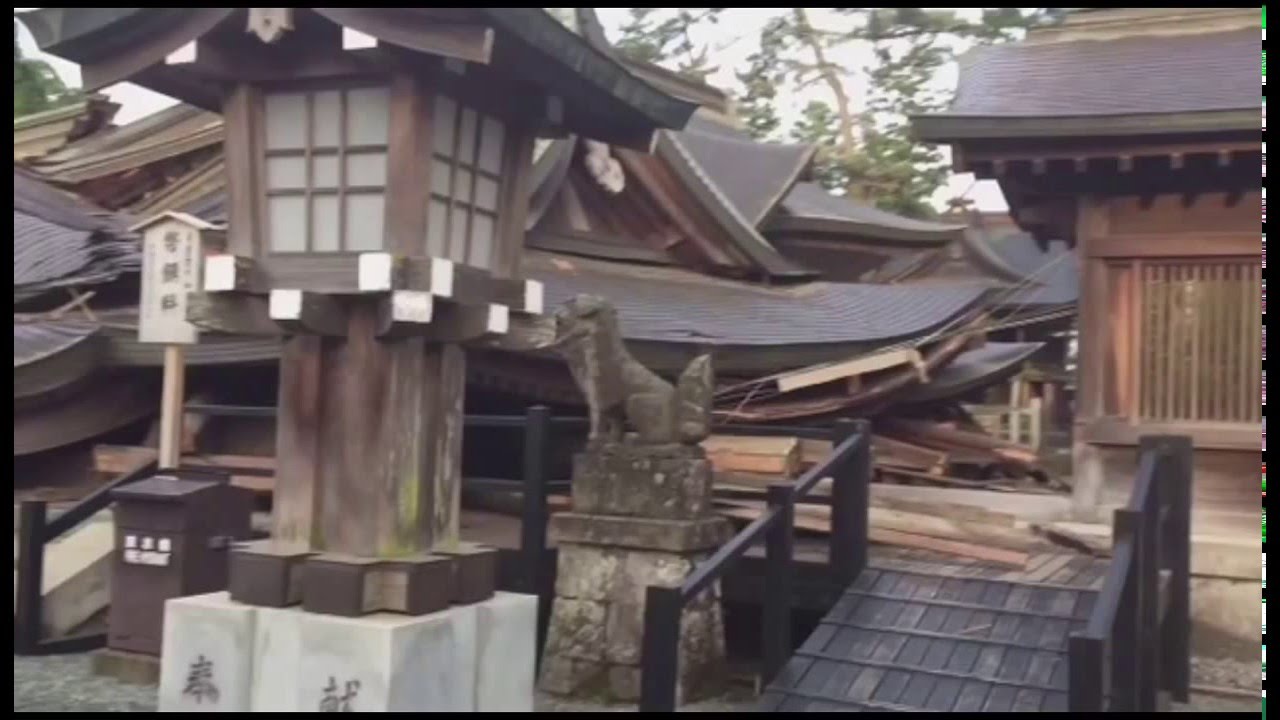
熊本地震被害状況Kumamoto earthquake damage situation20160416② YouTube

This Wallpaper is ranked 5 by BING for KEYWORD 地震, You will find this result at Bing.com.
Picture Details FOR 熊本地震被害状況Kumamoto earthquake damage situation20160416② YouTube's Picture| TITLE: | 熊本地震被害状況Kumamoto earthquake damage situation20160416② YouTube |
| IMAGE URL: | https://i.ytimg.com/vi/MNQd-pF8XMM/maxresdefault.jpg |
| THUMBNAIL: | https://tse4.mm.bing.net/th?id=OIP.ouTLLBS1OZMXs0Saw3uIxwHaEK&pid=Api&P=0&w=300&h=300 |
| IMAGE SIZE: | 99.2KB Bs |
| IMAGE WIDTH: | 1280 |
| IMAGE HEIGHT: | 720 |
| DOCUMENT ID: | OIP.ouTLLBS1OZMXs0Saw3uIxwHaEK |
| MEDIA ID: | resitem-4 |
| SOURCE DOMAIN: | www.youtube.com |
| SOURCE URL: | https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MNQd-pF8XMM |
| THUMBNAIL WIDTH: | 474 |
| THUMBNAIL HEIGHT: | 266 |
Related Images with 熊本地震被害状況Kumamoto earthquake damage situation20160416② YouTube
At least two perspectives of design undertaking are per the action-centric perspective. The two contain three ordinary activities.親子で地震対策(1)地震発生!そのときとる行動 NHK すくすく

地震情報 2020年09月07日 06時34分頃発生 最大震度:3 震源地:茨城

地震被害調査|地震被害調査|共通|飛島の技術|飛島建設

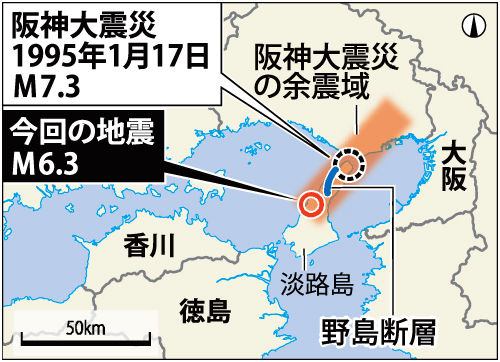
淡路島地震、阪神大震災とは「タイプ異なる」逆断層型 : スケ